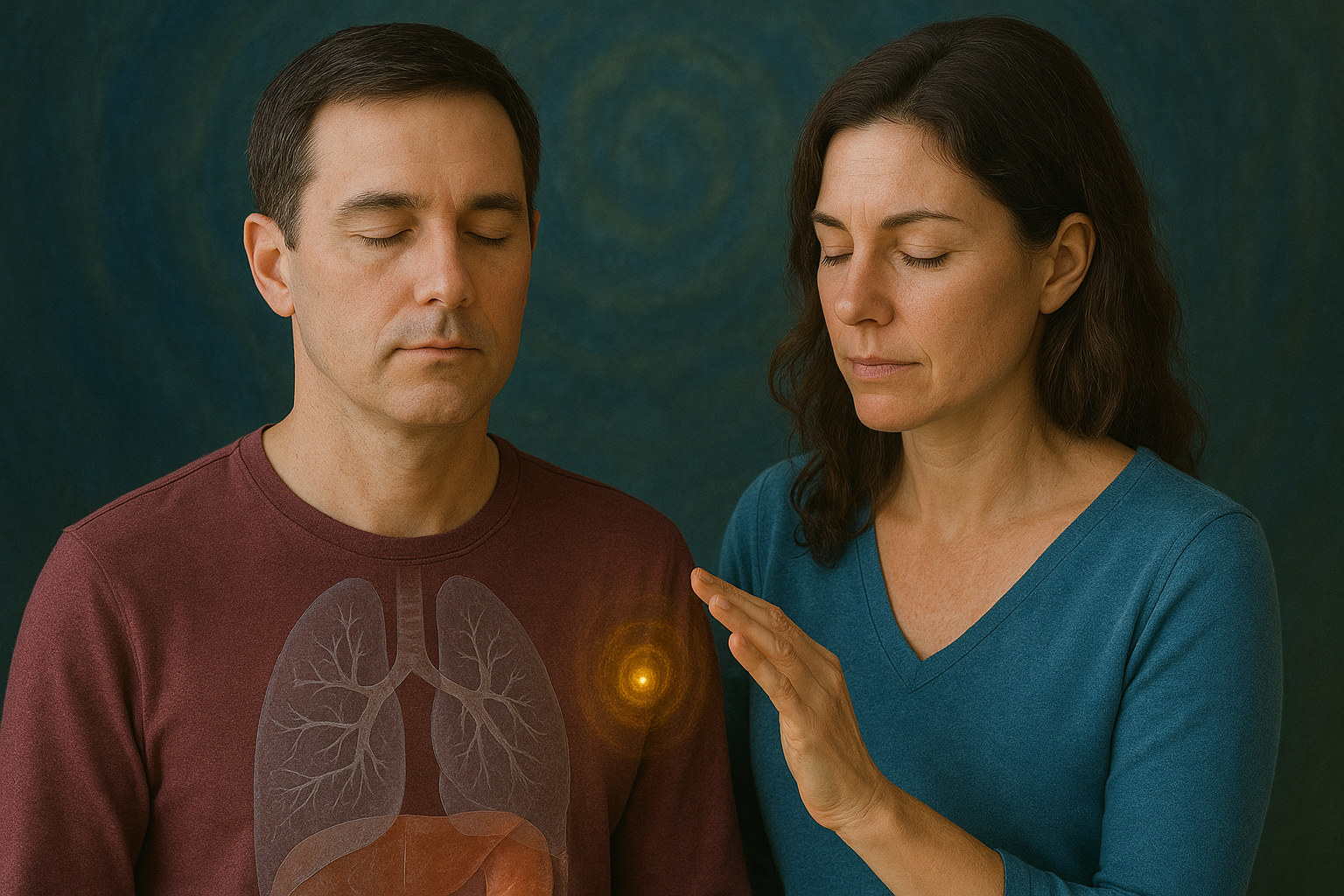
メディカルイントィティブとは何か
メディカルイントィティブとはエネルギーヒーリングでも特別に身体的な不調や病気に関することを的確に指摘出来、その上に自然治癒力を高め、心、メンタル健康のバランスを取っていくにはどうしたらよいのかをエネルギーヒーリングセッションでサポートするエネルギーワーカーを指します。
アメリカでは実際に医師と提携し、健康を取り戻す為に一緒に仕事をする人もいるのです。
メディカルイントィティブはどんなことをするのか
メディカルイントィティブは透視でエネルギー的に問題があるところが見える人もいれば、ハンドスキャンと言われる手をかざして感覚を探り、手で感じるエネルギーで問題をとらえる人もいます。
また手術後体内に残っている麻酔薬が不調を引き起こしている場合、麻酔薬を味で感じ取る人もいます。
つまり、エネルギーヒーラー(ワーカー)としてエネルギーを感じる感覚は人それぞれ開花し、頼るツールが異なるので一概にこうとは言えないのです。
一般的にエネルギーヒーリングで感じ取り、体の不調のセッションは大抵のエネルギーヒーラーなら出来ます。
しかしメディカルイントィブとはそれ以上、専門的に的確に問題があるところを指摘し、それをどうすればよいか、そして問題改善・解決に向け導いて行ける結果が出せる人の事を指します。
エネルギーヒーラーの中でも専門性があり、誰でもメディカルイントィブになれるわけではありません。
歴史的に良く知られているメディカルイントィブ例エドガーケイシー
世界的に良く知られ、そして多分メディカルイントィブとしての能力を発揮した人例ではエドガー・ケイシー氏があげられると思います。バージニア州には今でもエドガー・ケイシーが教えたことを学べる団体が存在し、講座などを受講したりする人も多いようです。
私の同僚の中でも講座を受講しに行った人もいました。
経歴
アメリカ合衆国ケンタッキー州ホプキンスビル出身。幼少期は聖職者になることを希望していた[1]。保険のセールスをしていたが、咽頭をこわし、会話がままならなくなり写真家に転向。この治療のために行われた催眠療法中に別の人格が現れ、自らの治療方法を述べ、その通りにすると症状は治った。他者の疾患の治療方法も答えることができ、心霊診断を行うようになった。1923年に印刷業者で宗教・哲学、特に近代神智学に詳しいアーサー・ラマース (Arthur Lammers) に出会い、ラマースは神智学の教えなどを催眠時のケイシーに質問し、ケイシーは神智学の影響を大きく受けた[1]。病気診断や前世診断、霊的なアドバイスを行い、バージニア州に病院を創立するも、短期間で廃業。有力者の親族の治療を行った際に新聞に掲載され一部で知られるようになったが、彼を紹介する本が出版される晩年まで一般ではさほど有名ではなかった[1]。
輪廻転生説を唱え、自分の前世はアトランティス人、ペルシアの王、トロイア出身の古代ギリシャの化学者であったと語った[4]。
1944年9月に脳卒中を引き起こし、1945年1月3日に死去した[5]。67歳没。それから3か月後、妻のガートルードもこの世を去った[6]。エドガー・ケイシーウィキペディアジャパンより
メディカルイントィブ検証・研究資料例
英語になりますが、メディカルイントィブに関してはこんな資料があります。
2020年全米直感医療協会のアンケート調査
THE USE OF MEDICAL INTUITION IN HEALTHCARE: a Survey by the National Organization for Medical Intuition
Maria T. Gentile, DO, CMIP; Tiffany Barsotti, PhD; Wendie Colter, MCWC, CMIP (2022)
The use of Medical Intuition has been recorded in clinical healthcare for more than two centuries, yet little is known about the practices and training of medical intuitives, or the use of Medical Intuition in healthcare. Although acknowledgement of Medical Intuition exists within the medical community (2005, Complementary and Alternative Medicine in the United States, IOM), scientific research on the skill is sparse, with only a handful of studies published over several decades. However, anecdotal accounts of medical intuitives working in clinical healthcare settings are common knowledge among professional medical intuitives.
The National Organization for Medical Intuition created a survey to gather information on the training, practices and uses of Medical Intuition, and sent it to over 300 self-identified professional medical intuitives in the United States. The results found:
82% of medical intuitives surveyed assist licensed healthcare professionals with Medical Intuition services for their patients and clients.
86% report receiving referrals from licensed medical professionals for Medical Intuition services.
30% identified themselves as licensed healthcare providers.
Download the complete report: “The Use of Medical Intuition in Healthcare”
Medical Intuition: A Qualitative Exploration of the Subjective Experience of Practitioners
Tracy L.W. Poff, PhD (2024)
Medical intuition practitioners purport to identify physical and nonphysical factors that contribute to an individual’s health condition, knowing nothing other than the person’s name. Using individual, semi-structured interviews, this qualitative study explored the experience of 15 self-identified medical intuitives.
Findings suggest that the nonlinear epistemic nature of medical intuition is additive and complementary to approaches used by conventional healthcare providers and that, together, a more complete picture of an individual’s health may be observed. Results of the study point to multiple areas for future research, as well as suggestions regarding methods of testing intuitive accuracy.
ASSESSING THE ACCURACY OF MEDICAL INTUITION
JOURNAL OF Integrative AND COMPLEMENTARY MEDICINE (JICM)Wendie Colter, MCWC, CMIP; Paul Mills, PHD (2020)
This exploratory study examined subjective accuracy and rates of acceptance of trained medical intuitives. Findings included a 94% accuracy rate of the Medical Intuitive’s ability to locate and evaluate the participant’s primary physical issue; 100% accuracy to locate a secondary physical issue (86% of participants responding); 98% accuracy in describing the participant’s life events, and 93% accuracy in describing a connection between the life events and health issues. Additionally, 94% (of 49% of the participants who responded to this question) indicated ‘‘Agree/Strongly Agree’’ that the medical intuitive was consistent with a known medical diagnosis.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2020.0244
INTUITIVE ASSESSMENTS: AN OVERVIEW
Daniel J. Benor, MD (2001)
Intuitives, including healers, are often able to obtain psychic impressions about people upon whom they focus their attention. These impressions may include information about the states of the subject’s body, emotions, mind, relationships and spiritual dimensions. Research on intuitive assessments is limited.
The development of intuitive awareness has far broader implications and applications beyond medical intuition. The process of knowing the world intuitively opens into an awareness of oneness with all creation, into realms that we have labeled as spiritual and mystical. This mode of knowing may be of enormous value in addressing some of the global crises challenging the continuation of our very existence on this planet.
Read more: https://www.danielbenor.com/intuitive-assessments-an-overview
Copyright © Daniel J. Benor, M.D. 2001 Reprinted with permission of the author P.O. Box 76 Bellmawr, NJ 08099 www.WholisticHealingResearch.com DB@danielbenor.com
Research
Colter, W., Mills, P. J. (2020). Assessing the Accuracy of Medical Intuition: A Subjective and Exploratory Study. Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine (New York, N.Y.), 26(12), 1130–1135.
Poff, T. L. W. (2024). Medical intuition: A qualitative exploration of the subjective experience of practitioners (Publication No. 31557026) [Doctoral dissertation, Sofia University]. ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global.
Wahbeh, H., Speirn, P., Yount, G. (2022, December). Extended Visual Perception Corroboration: A Pilot Study with Energy Medicine Reiki Practitioners. Integrative Medicine Reports 2023 2:1, 14-25
Mason, R. (2000, December). Expanding Diagnostic Vision with Medical Intuition, Interviews with Jay Caliendo, Medical Intuitive, and Abraham Kuruvilla, M.D., M.D.(H). Alternative and Complementary Therapies Journal, 331-336
Benor, D.J. (1992). Intuitive Diagnosis. Subtle Energies & Energy Medicine Journal, Vol 3, Number 2, pp. 41-64 https://journals.sfu.ca/seemj/index.php/seemj/article/viewFile/150/115
Jobst, K. A. (1997). One Man’s Meat Is Another Man’s Poison: The Challenge of Psychic/Intuitive Diagnosis to the Diagnostic Paradigm of Orthodox Medical Science. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 3(1), 1–3.
Burk, L., O’Brien, B., Charron, J. M., Sherman, K. J., & Bullock, M. L. (1997). Psychic/Intuitive Diagnosis: Two Case Reports and Commentary. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 3(3), 209–211.
Liem, T. (2017, Sep 1). Intuitive Judgment in the Context of Osteopathic Clinical Reasoning. Journal of the American Osteopath Association, 117(9):586-594. doi: 10.7556/jaoa.2017.113
Melin-Johansson, C., Palmqvist, R. & Rönnberg, L. (2017, Mar 22). Clinical Intuition in the Nursing Process and Decision-Making – a Mixed-Studies Review. Journal of Clinical Nursing. doi: 10.1111/jocn.13814
Roseman-Halsband, J. L., Marcow Speiser, V., & Lafferty, L. (2017). Intuition in Medicine. Alternative and Complementary Therapies, 23(6), 231–235;
Hassani, P., Abdi., A., Jalali, R. & Salari, N. (2016, Feb 10). Use of Intuition by Critical Care Nurses: a Phenomenological Study. Advances in Medical Education and Practice, Volume 7, 65-71 https://www.dovepress.com/use-of-intuition-by-critical-care-nurses-a-phenomenological-study-peer-reviewed-article-AMEP
Mickelborough, Tim (Oct. 1, 2015). Intuition in Medical Practice: A Reflection on Donald Schön’s Reflective Practitioner. Medical Teacher, Volume 37, Issue 10
Woolley, A., & Kostopoulou, O. (2013). Clinical Intuition in Family Medicine: More than First Impressions. Annals of Family Medicine, 11(1), 60–66. https://doi.org/10.1370/afm.1433
Green, C., (2012). Nursing Intuition: A Valid Form of Knowledge. Blackwell Publishing Ltd. Nursing Philosophy, 13, pp. 98–111.
Miller, E.M. & Hill, P.D. (2017, Aug). Intuition in Clinical Decision Making: Differences Among Practicing Nurses. Journal of Holistic Nursing. 1:898010117725428. doi: 10.1177/0898010117725428
Peterkin, Alan MD, (2017, April 10). Physician Intuition. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 189(14): E544. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5386850/
Lufityanto, G., Donkin, C., & Pearson, J. (2016). Measuring Intuition: Nonconscious Emotional Information Boosts Decision Accuracy and Confidence. Psychological Science. doi: 10.1177/0956797616629403
Pretz, et al (2014). Development and Validation of a New Measure of Intuition: the Types of Intuition Scale. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 27, 454-467
Marks-Tarlow, T. (2012). Clinical Intuition in Psychotherapy: The Neurobiology of Embodied Response (Norton Series on Interpersonal Neurobiology) (Illustrated ed.). W. W. Norton & Company. (pp.3, 30, 32, 42, 163, 188)
Schwarzkopf, D. S. (2014). We Should Have Seen This Coming. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00332.
Cork, L.L., (2014). Nursing Intuition as an Assessment Tool in Predicting Severity of Injury in Trauma Patients. Journal of Trauma Nursing 21(5): 244-252.
Amoils, S. (2002). The Diagnostic Validity of Human Electromagnetic Field (Aura) Perception. Medical Acupuncture, 13(2), 25–28.
Greenhalgh, T. (2002). Intuition and Evidence – Uneasy Bedfellows? The British Journal of General Practice: The Journal of the Royal College of General Practitioners, 52(478), 395–400.~National Organization for Medical Intuition
邦訳しますと
医療直観のヘルスケアにおける活用
全米医療直観協会による調査
Maria T. Gentile, DO, CMIP; Tiffany Barsotti, PhD; Wendie Colter, MCWC, CMIP (2022)
医療直観(Medical Intuition)の活用は200年以上にわたり臨床医療の現場で記録されていますが、医療直観者の実践や訓練方法、またヘルスケアにおける医療直観の利用についてはほとんど知られていません。医療直観の存在は医学界でも認められています(2005年『米国における補完代替医療』医学研究所報告)。しかし、科学的研究は乏しく、数十年間でわずかな研究しか発表されていません。それにもかかわらず、臨床現場で医療直観者が活動していることは、専門的な医療直観者の間では広く知られています。
全米医療直観協会は、医療直観の訓練・実践・利用に関する情報を収集するために調査を作成し、米国内で300名以上の自称プロの医療直観者に送付しました。その結果は以下の通りです:
-
回答者の82%が、患者やクライアントに対して医療直観サービスを提供する際、ライセンスを持つ医療従事者を支援していると回答。
-
86%が、ライセンスを持つ医療従事者から医療直観サービスの紹介を受けていると回答。
-
30%が、自身をライセンスを持つ医療従事者であると認識していると回答。
完全版レポートをダウンロード: The Use of Medical Intuition in Healthcare
医療直観:実践者の主観的体験に関する質的探究
Tracy L.W. Poff, PhD (2024)
医療直観の実践者は、対象者の名前以外は何も知らない状態で、その人の健康状態に影響を与える物理的および非物理的要因を特定できると主張しています。本研究は15人の自称医療直観者への半構造化インタビューを用いて、その体験を質的に探究しました。
結果は、医療直観の非線形的な認識の特性が、従来のヘルスケア提供者が用いるアプローチを補完・拡張することを示唆しており、両者を組み合わせることで、より包括的な健康の全体像を把握できる可能性があることを示しました。また、今後の研究における複数の課題や、直観の正確性を検証するための方法論についての提案も示されました。
医療直観の正確性評価
『Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine (JICM)』
Wendie Colter, MCWC, CMIP; Paul Mills, PhD (2020)
本探索的研究では、訓練を受けた医療直観者の主観的な正確性および受容率を検証しました。
主な結果は以下の通りです:
-
参加者の主要な身体的問題を特定・評価する能力で94%の正確性。
-
二次的な身体的問題を特定する能力で100%の正確性(回答者の86%)。
-
参加者の人生の出来事を説明する能力で98%の正確性。
-
人生の出来事と健康問題との関連を説明する能力で93%の正確性。
-
さらに、回答した参加者の49%のうち94%が「同意/強く同意」と答え、医療直観者の評価が既知の医学的診断と一致していたことを示しました。
詳細はこちら: https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2020.0244
直観的評価:概要
Daniel J. Benor, MD (2001)
ヒーラーを含む直観者は、注目した対象者について霊的印象を得ることがしばしば可能です。これには身体、感情、心、対人関係、霊的次元の状態に関する情報が含まれる場合があります。しかし、直観的評価に関する研究は限られています。
直観的認識の発達は、医療直観を超えた広範な意味と応用を持ちます。直観的に世界を知るプロセスは、すべての創造物との一体感を自覚し、霊的・神秘的な領域に踏み入れることにつながります。この知の様式は、人類の存続を脅かす地球規模の危機に取り組むうえで非常に価値があるかもしれません。
詳細はこちら: https://www.danielbenor.com/intuitive-assessments-an-overview
© Daniel J. Benor, M.D. 2001 著者の許可を得て再掲載
P.O. Box 76 Bellmawr, NJ 08099 www.WholisticHealingResearch.com DB@danielbenor.com
研究文献一覧
-
Colter, W., Mills, P. J. (2020). Assessing the Accuracy of Medical Intuition: A Subjective and Exploratory Study. Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine (New York, N.Y.), 26(12), 1130–1135.
-
Poff, T. L. W. (2024). Medical intuition: A qualitative exploration of the subjective experience of practitioners (Publication No. 31557026) [Doctoral dissertation, Sofia University]. ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global.
-
Wahbeh, H., Speirn, P., Yount, G. (2022, December). Extended Visual Perception Corroboration: A Pilot Study with Energy Medicine Reiki Practitioners. Integrative Medicine Reports 2023 2:1, 14-25
-
Mason, R. (2000, December). Expanding Diagnostic Vision with Medical Intuition. Alternative and Complementary Therapies Journal, 331-336
-
Benor, D.J. (1992). Intuitive Diagnosis. Subtle Energies & Energy Medicine Journal, Vol 3, Number 2, pp. 41-64
-
Jobst, K. A. (1997). One Man’s Meat Is Another Man’s Poison: The Challenge of Psychic/Intuitive Diagnosis to the Diagnostic Paradigm of Orthodox Medical Science. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 3(1), 1–3.
-
Burk, L., O’Brien, B., Charron, J. M., Sherman, K. J., & Bullock, M. L. (1997). Psychic/Intuitive Diagnosis: Two Case Reports and Commentary. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 3(3), 209–211.
-
Liem, T. (2017). Intuitive Judgment in the Context of Osteopathic Clinical Reasoning. Journal of the American Osteopath Association, 117(9):586-594.
-
Melin-Johansson, C., Palmqvist, R. & Rönnberg, L. (2017). Clinical Intuition in the Nursing Process and Decision-Making. Journal of Clinical Nursing.
-
Roseman-Halsband, J. L., et al. (2017). Intuition in Medicine. Alternative and Complementary Therapies, 23(6), 231–235.
-
Hassani, P., et al. (2016). Use of Intuition by Critical Care Nurses. Advances in Medical Education and Practice, 7, 65-71.
-
Mickelborough, T. (2015). Intuition in Medical Practice: A Reflection on Donald Schön’s Reflective Practitioner. Medical Teacher, 37(10).
-
Woolley, A., & Kostopoulou, O. (2013). Clinical Intuition in Family Medicine. Annals of Family Medicine, 11(1), 60–66.
-
Green, C. (2012). Nursing Intuition: A Valid Form of Knowledge. Nursing Philosophy, 13, 98–111.
-
Miller, E.M. & Hill, P.D. (2017). Intuition in Clinical Decision Making. Journal of Holistic Nursing.
-
Peterkin, A. (2017). Physician Intuition. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 189(14): E544.
-
Lufityanto, G., et al. (2016). Measuring Intuition. Psychological Science.
-
Pretz, et al (2014). Development and Validation of a New Measure of Intuition. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 27, 454-467.
-
Marks-Tarlow, T. (2012). Clinical Intuition in Psychotherapy. W. W. Norton & Company.
-
Schwarzkopf, D. S. (2014). We Should Have Seen This Coming. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8.
-
Cork, L.L. (2014). Nursing Intuition as an Assessment Tool in Predicting Severity of Injury in Trauma Patients. Journal of Trauma Nursing 21(5): 244-252.
-
Amoils, S. (2002). The Diagnostic Validity of Human Electromagnetic Field (Aura) Perception. Medical Acupuncture, 13(2), 25–28.
-
Greenhalgh, T. (2002). Intuition and Evidence – Uneasy Bedfellows? The British Journal of General Practice, 52(478), 395–400.
こちらのリンクが資料元です。
2024年の代替医療と補充医療ジャーナルの研究資料
The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicineと呼ばれる信頼された研究資料データが発表されるところでの研究資料結果にこんなものがあります。
Abstract
Background:Medical Intuition is a system of expanded perception gained through the human sense of intuition. Medical Intuition focuses on visualization skills and intuitive and innovative scanning to obtain information from the physical body and its energy systems. Medical Intuition is designed to assist health care providers in a cost-effective, targeted approach to a patient’s presenting concerns, and is not meant to serve as a diagnosis of illness or disease.Objectives:This exploratory study examined subjective accuracy and rates of acceptance of trained Medical Intuitives.Settings:Sixty-seven adult women and men served as study participants.Procedure:The procedure for each medical intuition session was standardized. Thirty or 60-min sessions were conducted by phone or video. The participant verbally provided their name at the beginning of the session. The Medical Intuitives were instructed not to engage in any conversation with the participant other than telling them the information they were “seeing” during the scanning process. Following the session, each participant completed an anonymous online standardized case report form documenting their assessment of the reading.Results:Findings included a 94% accuracy rate of the Medical Intuitive’s ability to locate and evaluate the participant’s primary physical issue; 100% accuracy to locate a secondary physical issue (86% of participants responding); 98% accuracy in describing the participant’s life events, and 93% accuracy in describing a connection between the life events and health issues.Conclusions:These initial findings suggest that trained Medical Intuitives have strong subjectively reported accuracy rates identifying primary and secondary health issues and that their services are positively evaluated in the context of an individual’s concerns regarding their health.~The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine
要旨
背景:
メディカル・インテュイション(Medical Intuition)とは、人間の直感を通じて得られる拡張的知覚の体系です。メディカル・インテュイションは、可視化スキルや直感的・革新的なスキャニングに焦点を当て、身体およびそのエネルギーシステムから情報を得るものです。これは、医療従事者が患者の主訴に対して費用対効果の高い的確なアプローチを行うために設計されており、病気や疾患の診断を目的とするものではありません。
目的:
本探索的研究では、訓練を受けたメディカル・インテュイティブ(Medical Intuitive)の主観的な正確性および受容率を検証しました。
対象:
67名の成人男女が研究参加者として従事しました。
手順:
各セッションの手順は標準化されました。30分または60分のセッションが電話またはビデオで実施されました。参加者はセッション開始時に口頭で自分の名前を伝えました。メディカル・インテュイティブは、スキャン中に「見えている」情報を伝える以外、参加者との会話をしないよう指示されました。セッション後、各参加者は匿名のオンライン標準化ケース報告フォームに回答し、リーディングの評価を記録しました。
結果:
主な結果は以下の通りです。
-
参加者の主要な身体的問題の特定および評価において 94% の正確性。
-
二次的な身体的問題の特定において 100% の正確性(回答者の86%)。
-
参加者の人生の出来事の記述において 98% の正確性。
-
人生の出来事と健康問題の関連性の記述において 93% の正確性。
結論:
これらの初期的な結果は、訓練を受けたメディカル・インテュイティブが、主要および二次的な健康問題を特定する上で高い主観的正確性を示していること、またそのサービスが健康に関する個人の懸念の文脈において肯定的に評価されていることを示唆しています。
こちらが資料元リンクです。
最後に
メディカルイントィブとはエネルギーヒーラーの中でも医療関係等を専門にする人達です。一般の体の不調を改善するエネルギーヒーリングよりもより的確な判断が出来、アメリカでは医療関係者たちと仕事をしたり、口コミ紹介で仕事をしている人達も大勢います。
日本ではまだ盛んになっていないでしょうが、情報が隠せない現在、ようやく補充的な役割としてのエネルギーヒーリングと医療の関連性が否定できない事であることを資料を含めて紹介させて頂きました。









